Exclusion from
“Residential Building” code
Ministry of Power, Government of India launched the ECO Niwas Samhita in December 2018, which is an Energy Conservation Building Code for Residential Buildings (ECBC-R). It aims to benefit the occupants and the environment by promoting energy efficiency in design and construction of single and multi-dwelling units.
Scope and Requirement
Ministry of Power, Government of India launched the ECO Niwas Samhita 2018, which is an Energy Conservation Building Code for Residential Buildings (ECBC-R). The implementation of this Code will provide a fillip to energy efficiency in residential sector. It aims to benefit the occupants and the environment by promoting energy efficiency in design and construction of single and multi-dwelling units.
The provisions of this code apply to all residential buildings and residential parts of mixed land-use projects, both built on a plot area of ≥500 m2. However, the actual plot area is subjective to the respective states and municipal bodies on the prevalence in their area of jurisdiction.
Area of the buildings in residential space and energy consumption forecast
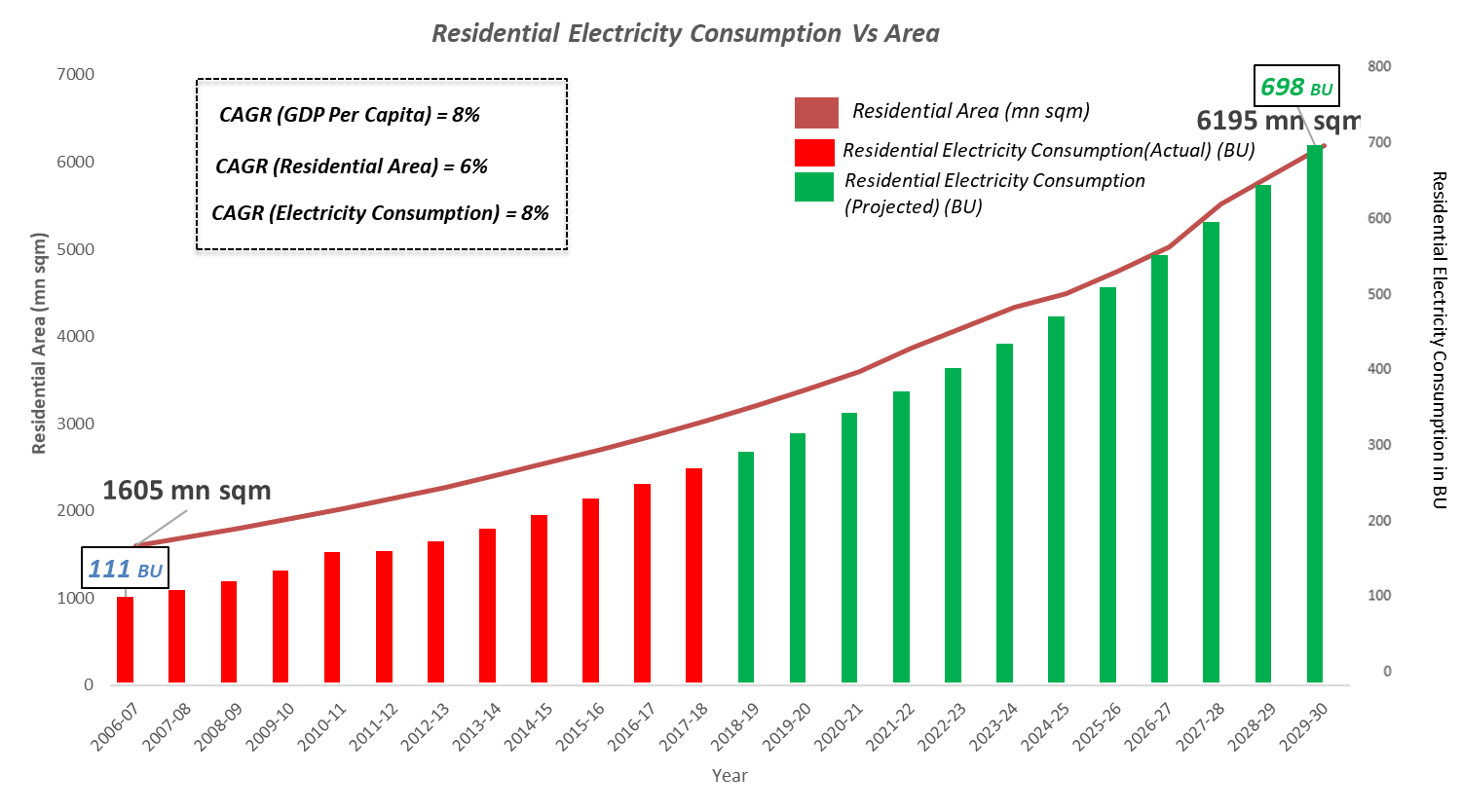
Urbanization and high GDP growth rate has fueled the electricity consumption in residential sector as well2. Electricity demand in residential sector has been increasing at a CAGR of 8% per year on average. This robust growth shall lead to an increase in electricity consumption from 2730 BU in 2017[ Energy statistics, 2019- MoSPI] to almost 700 BU in 2030.
Building components covered
Energy Conservation Building Code – Residential (ECBC-R) (Part I: Building Envelope) sets the minimum building envelope performance standards to limit heat gains and to limit heat loss, as well as for ensuring adequate natural ventilation and daylighting potential. The code provides design flexibility to innovate and vary important envelope components such as wall type, window size, type of glazing, and external shading to windows to meet the compliance.
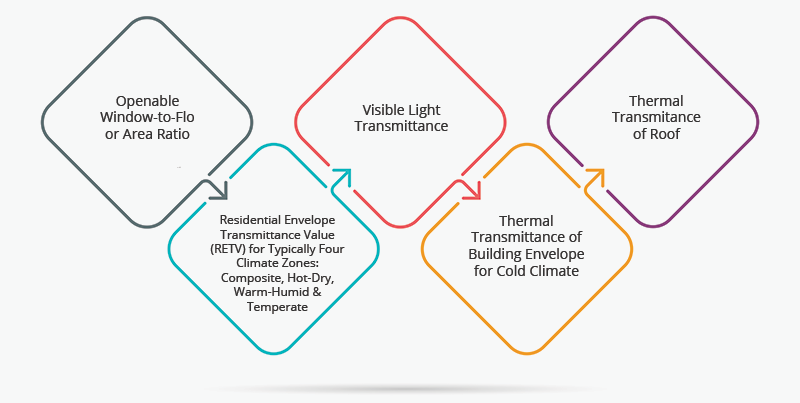
Key components of ENS part-1 building envelope
Eco Niwas Samhita (ENS), Part -2 The intent of Eco Niwas Samhita 2021, specifically focusing on Code Compliance and Part-II: Electromechanical and Renewable Energy Systems (ENS-C&2), is to ensure adherence to the code and establish the minimum requirements for building services.
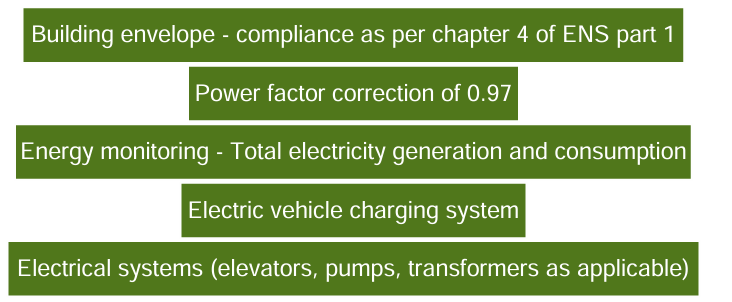
Key components of ENS part 2
ENS Level of compliance
To demonstrate compliance with the ENS code, the residential building shall comply with all mandatory requirements. The code defines the minimum ENS score required for low-rise buildings, affordable housing, and high-rise residential buildings.
Saving Calculation
The methodology adopted for estimating savings is based on RETV calculations. Residential envelope heat transmittance (RETV) is the net heat gain rate (over the cooling period) through the building envelope (excluding the roof) of the dwelling units divided by the area of the building envelope (excluding the roof) of the dwelling units. Its unit is W/m2.
As per ENS part 1, the RETV for the building envelope (except the roof) in different climate zones:
